ECG Signal Construction From Heart Sounds via Single Node, Surface Acoustic Sensing
Kaylee (Yaxuan) Li, Yasha Iravantchi, Hyunmin Park, Yiming Liu, and Alanson Sample
Abstract
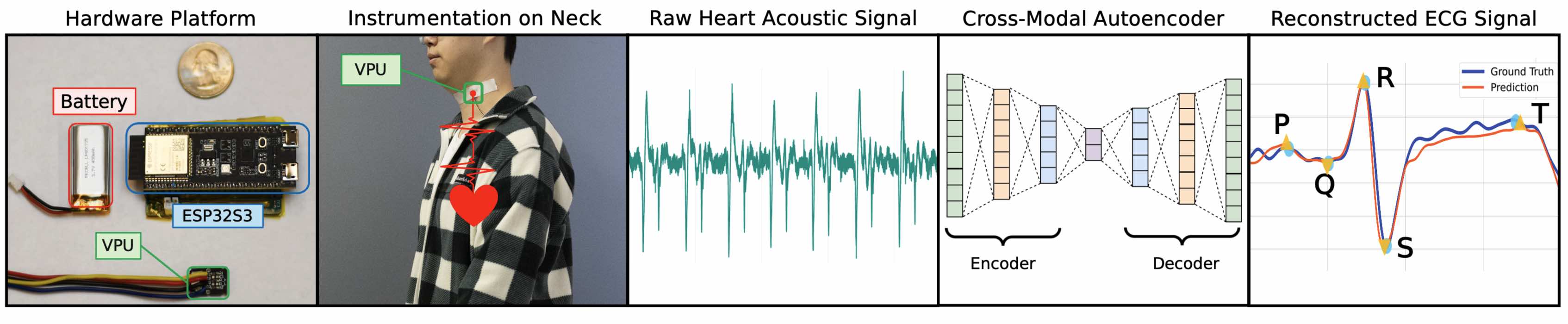
Effective means of enabling single-lead, non-intrusive, and dry electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements offer the potential for prolonged cardiac rhythm monitoring of mobile users in non-clinical environments. However, existing ECG measurement approaches require accurate electrode placement, cumbersome wiring, and require users to be stationary. Alternatively, current heart sound-based approaches such as phonocardiograms lack the sensitivity and precision to detect crucial cardiac rhythm features and are vulnerable to environmental noise. This work utilizes a wide bandwidth surface-acoustic-wave microphone on the neck to capture heart sounds via the carotid artery. A cross-modal autoencoder, a state-of-the-art algorithm for signal modality conversion, is proposed to transform heart acoustic signals into corresponding ECG waveforms. Results from a 9 participant study demonstrate the effectiveness of constructing a PQRST waveform from acoustic heart sounds and accurately determining critical PQRST metrics. Finally, mobile acoustic ECG wave construction of a user walking is demonstrated, laying the groundwork for unobtrusive, long-term, low-cost daily cardiac rhythm monitoring.
